Social Determinants of Inuit Health
Definition
As defined in World Health Organization documents, the social determinants of health focus on the lifelong importance of health determinants in early childhood, and the effects of poverty, drugs, working conditions, unemployment, social support, food security and policy on populations.
Research Purpose
A significant health gap exists in Canada between Inuit and non-Inuit Canadians. Inuit suffer much lower life expectancies than other Canadians, comparatively high rates of infant mortality, the highest suicide rates of any group in Canada, and disproportionately higher rates of chronic illness and infectious disease, heart disease, diabetes, and respiratory illness. Existing research suggests that this health gap in many respects is a symptom of poor socioeconomic conditions in Inuit communities which are characterized by high poverty rates, low levels of education, limited employment opportunities, and inadequate housing conditions.
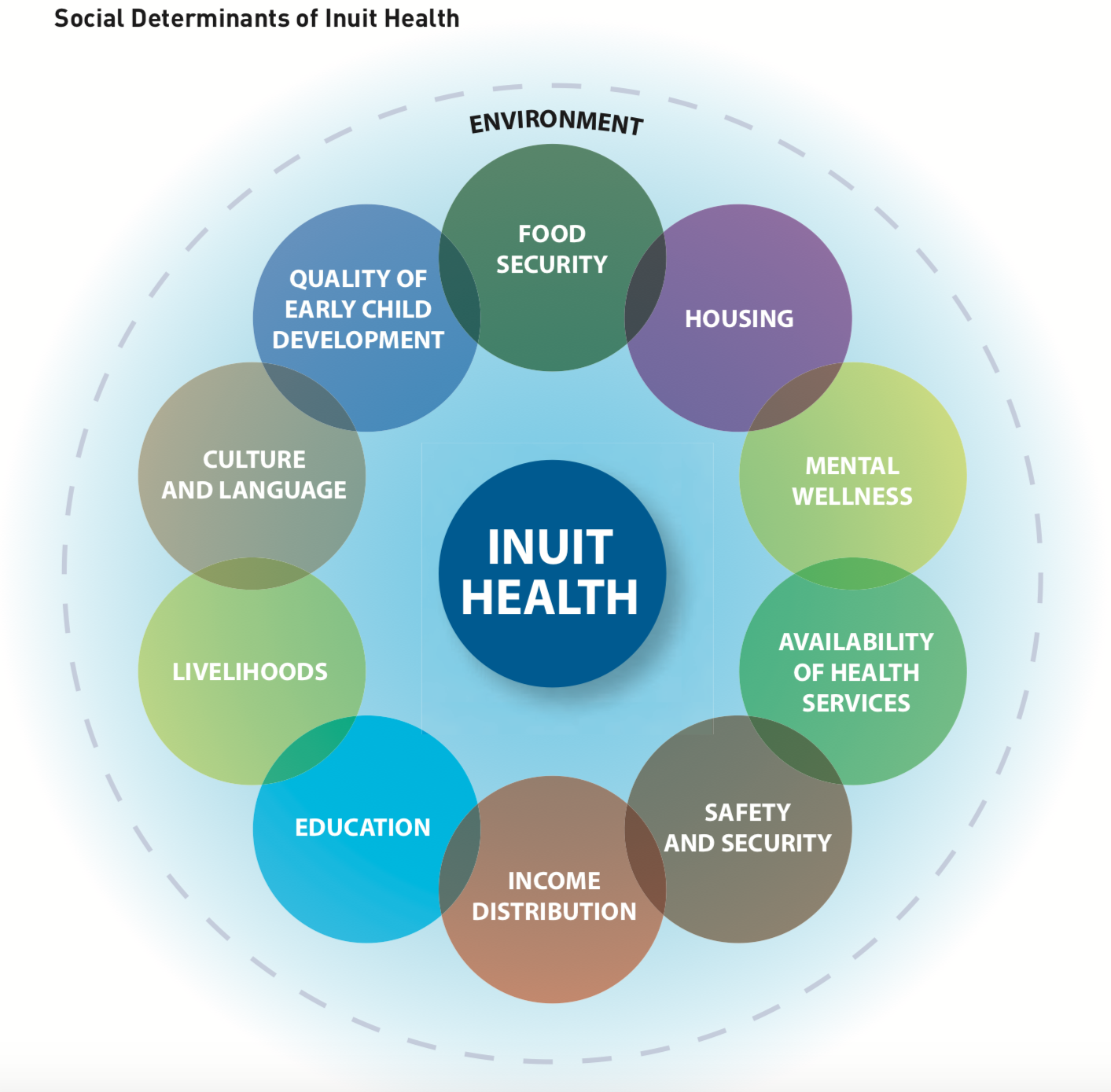
Inuit take a holistic view of health and strongly believe that significant improvements to Inuit health can be made by addressing current socioeconomic conditions that are a direct result of the historical changes that occurred over the last 60 years.
ITK has a pivotal role in supporting pan-Inuit research and advocacy at the international and national level with governments and funders toward policies and initiatives that are Inuit-specific and improve health conditions in Inuit communities. Read the policy background on each social determinant of health and see what efforts and interventions are being made to improve the quality of life for Inuit.
INSTRUCTIONS:
As a CSW and Manager working with clients and organizations advancing programs, services and client activities, it is vital that you read the full report to be aware of the categories examined within social determinants of health and what is currently affecting Inuit. You will also need to refer to it for the Final Quiz.

Copyright © All Rights Reserved

