Greenhouse Effect
The Greenhouse Effect is one of the major contributors of climate change. By definition, the Greenhouse Effect refers to the overall increase in the global climate that is caused by the harmful gases which are released into the Earth’s atmosphere.
What are some sources of greenhouse gases?
There are both natural and human sources of greenhouse gases:
- NATURALLY-OCCURRING - forest fires, volcanoes
- HUMAN-CAUSED - using fossil fuels and energy like driving a car, taking an airplane, using electricity to watch television, charging our phone, heating our homes and businesses.
These harmful gases, often referred to as ‘Greenhouse Gases’, form a thick layer in the upper atmosphere of our planet. Greenhouse Gases essentially consist of Carbon Dioxide (CO2), Methane (CH4), and Nitrous Oxide (N2O). They are emitted through the burning of fossil fuels such as gasoline, diesel and coal.
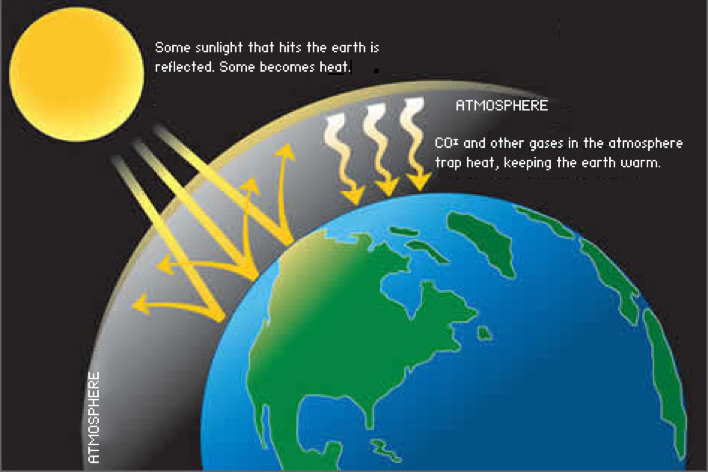
When sunlight enters the planet’s atmosphere, the rays radiate in different directions throughout the Earth’s surface. Some of these rays naturally get absorbed by the surface whereas others reflect back into space. However, the thick layer of greenhouse gases prevent these rays from exiting the Earth’s atmosphere, thereby leading them to deflect back onto the surface. As a result, the surface is forced to absorb a greater intensity of sunlight, thus, raising the overall temperature of the planet.
Greenhouse gases are made of molecules that have parts that can vibrate and move as it interacts with electromagnetic energy. The major greenhouse gases like methane (CH4), carbon dioxide (CO2), and water (H2O), absorb energy store it as motion and vibration. These same gases can also release energy into the environment by slowing down this vibration and releasing this same energy.
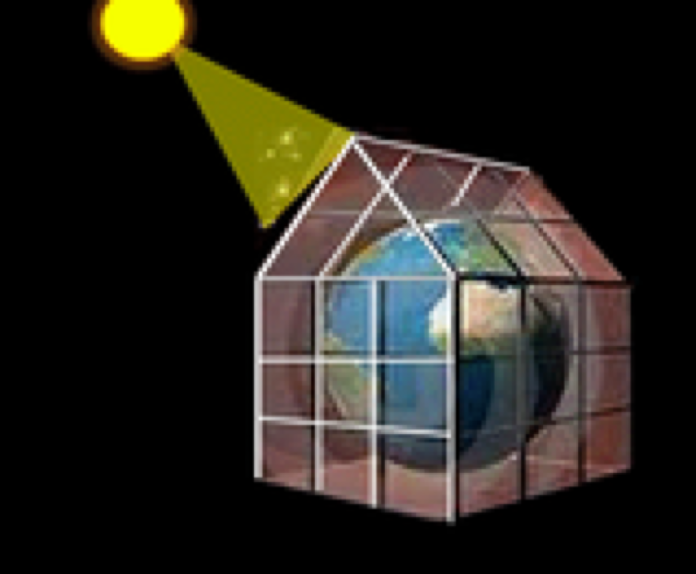
Why is it called the "Greenhouse Effect?"
One of the main reasons as to why this process is called the “Greenhouse Effect” is because it operates in a similar manner to the greenhouse shed. The greenhouse shed is a special agricultural house-like container which enables heat to pass inside it but prevents it from leaving. This process is highly successful when it comes to growing certain plants that require high intensity of heat in order to grow. The overall atmosphere of the Greenhouse shed considerably increases as the heat begins to accumulate, thereby raising the temperature of the surrounding environment.
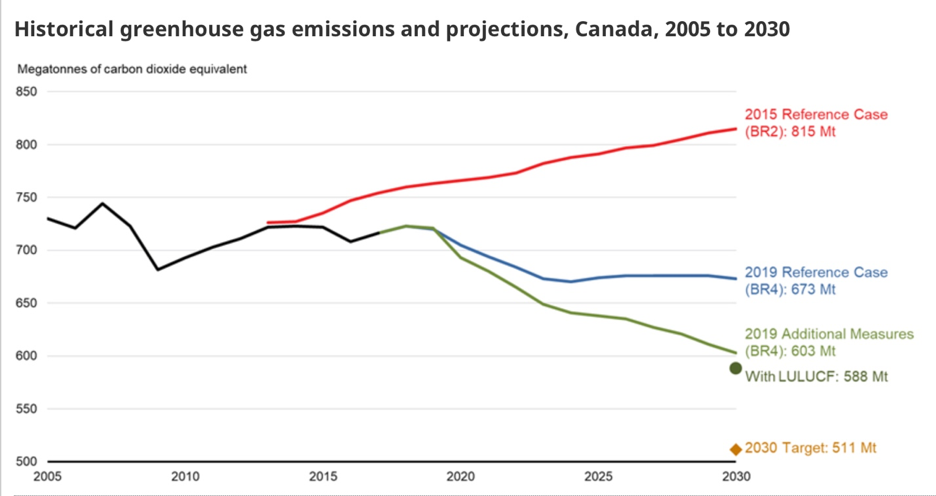
When the overall temperature of the surface rises at an exponential rate, extreme weather conditions become more frequent. In different parts of the world, we get to witness extreme heat or cold weathers which either lead to droughts or floods, depending upon the weather. One such instance of this unusual weather is occurring in the Arctic sea ice where glaciers, on a massive scale, have begun to melt down because of the overall increase in temperature. The Arctic is mainly made up of frozen surface upon which, a number of animal species survive.

Copyright © All Rights Reserved

